Insulin injection and oral hypoglycemic drugs:
Unable to completely restore glycemic control, prone to development of irreversible complications eg: retinopathy, nephropathy, and peripheral neuropathy. A major burden of self-care.
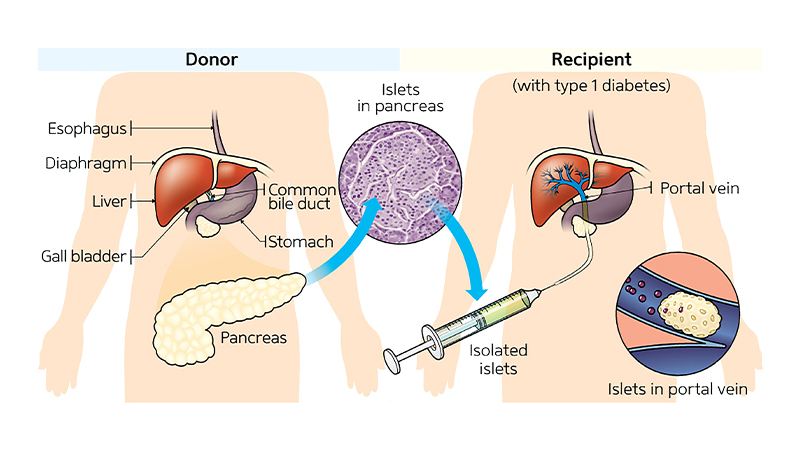
Islet transplantation:
Scarcity of cadaveric donor islets, requires immunosuppression.
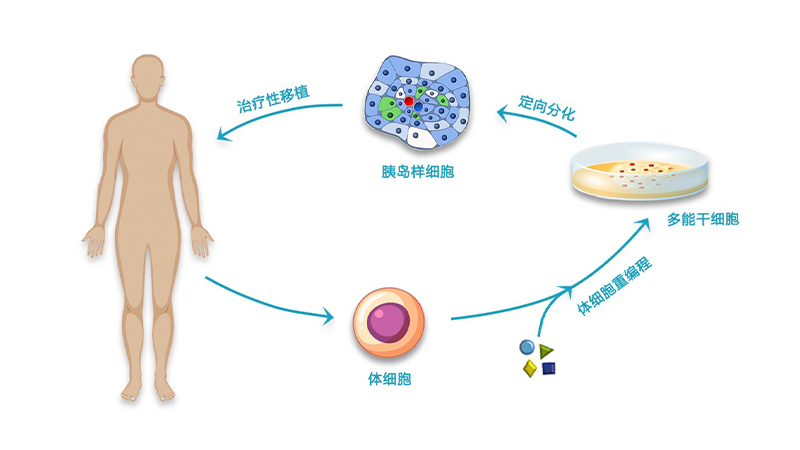
Leveraging human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) as an unlimited source of pancreatic
islet cells for clinical islet transplantation.
Realizing large-scale, standardized and industrialized production of pancreatic islet cells.